Bodies© INCorporated
Victoria Vesna
1996
The representation of the self through digital avatars became an increasingly important cultural practice in the 1990s, first in text-based chat rooms like LambdaMOO and later in graphical ones such as The Palace. These onscreen alter egos promised self-expression and an opportunity to explore alternative bodily forms, but in doing so, they often played into existing stereotypes and markers of social status.
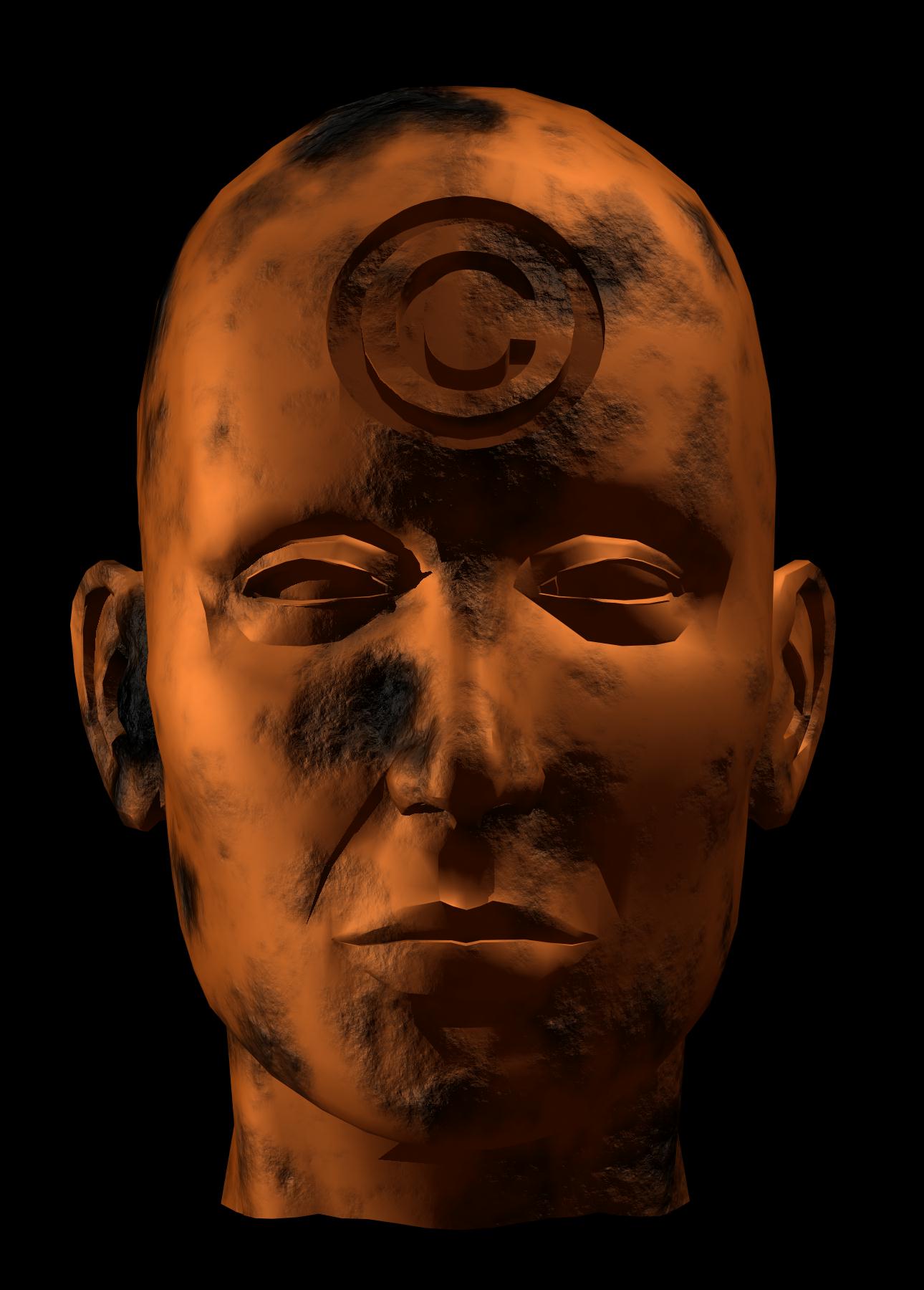
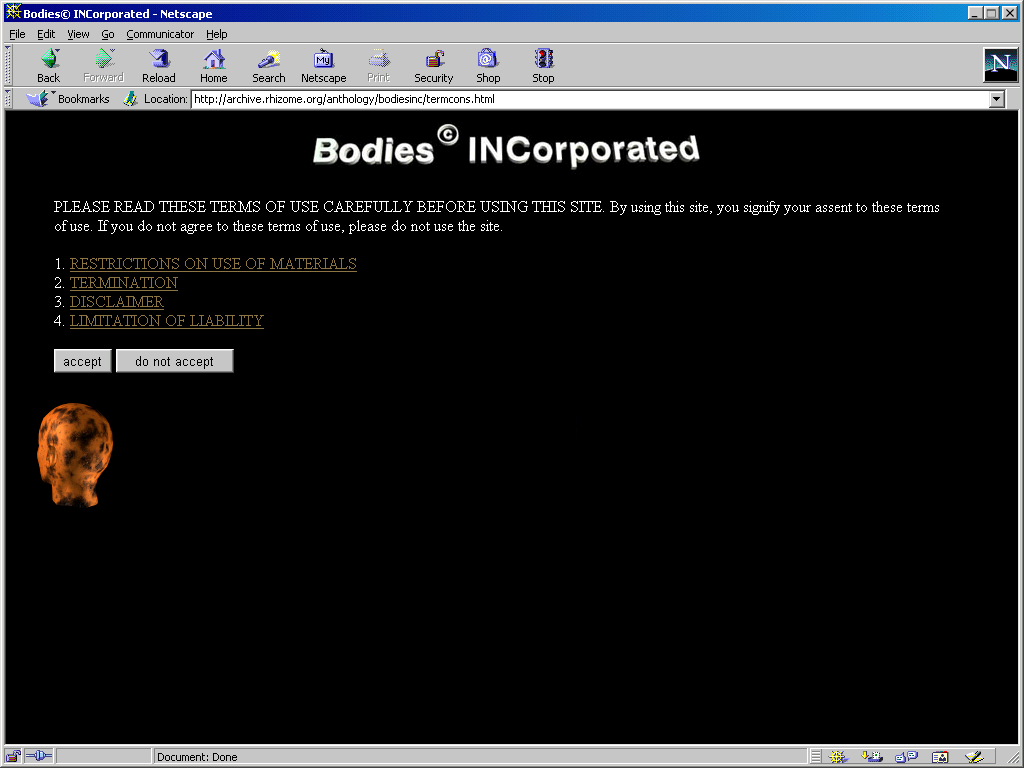
Victoria Vesna’s Bodies© INCorporated responded to this set of conditions by offering users the opportunity to create their own avatar on a site that emphasized the customizable digital body as commercial asset. Presented online and in a gallery installation, Bodies© INCorporated allowed users to construct 3D digital avatars in VRML (Virtual Reality Modeling Language) from an assemblage of body parts of various genders, sizes, and ages, but only after the user clicked through extensive terms and conditions, forfeiting all rights and ownership.
By adopting and heightening the corporate aesthetics of the early web, Vesna raised questions that artists still grapple with today: What value does the articulation of identity have, when one must work within the options defined by consumer culture? Is amplifying and making visible the effects of capitalism an effective form of critique? Or does it just reinforce its conditions?
“One thing is certain—the avatar business is booming.”
—Victoria Vesna
Visit work
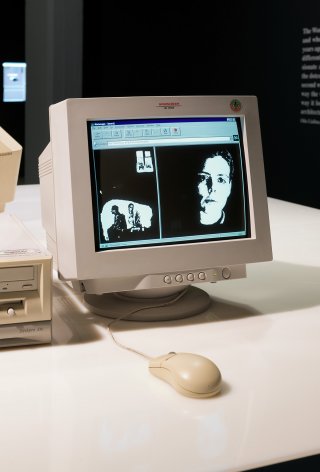
In 1995, Victoria Vesna posted a “Body Construction Order Form” on the website for her project Virtual Concrete, which also included a gallery installation and a CU-SeeMe webcam. “Construct a body to suit your individual likes and dislikes,” the page offered, asking users to supply a name, gender, and describe what their body meant to them.
 Virtual Concrete at Huntington Beach Arts Center, 1995.
Virtual Concrete at Huntington Beach Arts Center, 1995.
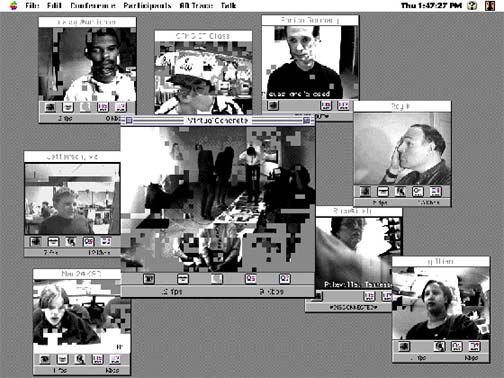 Image of remote audience for Virtual Concrete.
Image of remote audience for Virtual Concrete.
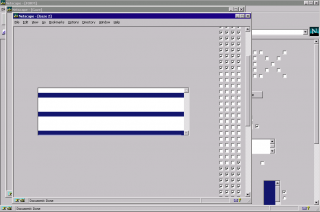
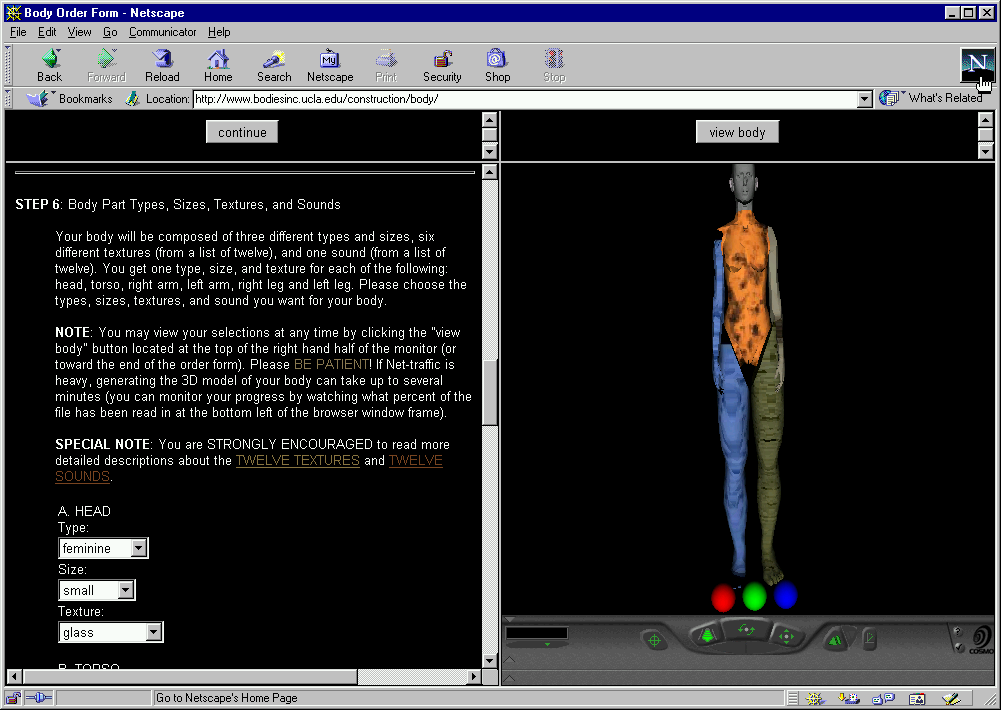
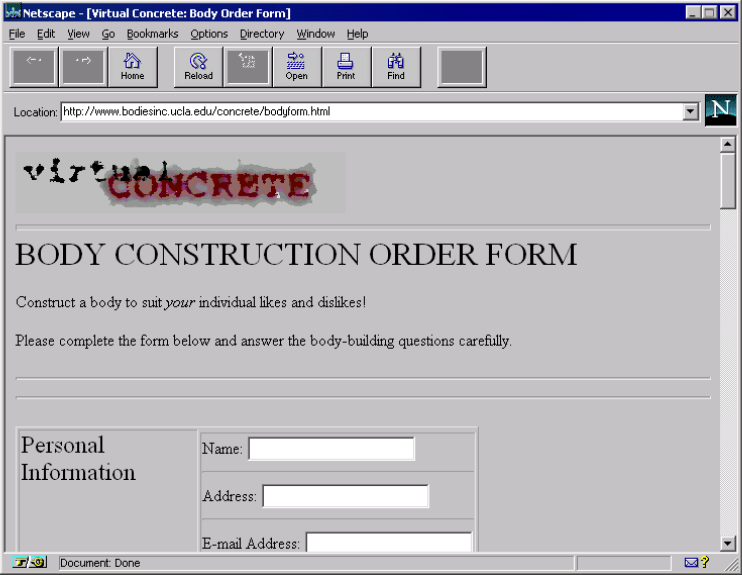 Screenshot of body construction order form.
Screenshot of body construction order form.
Within two weeks, more than one thousand orders had been submitted. Vesna had intended for the project to function as a forum for discussion, but soon she was receiving demands from users who expected to receive their graphical avatars.
This inspired Vesna to create a platform that would allow people to construct and interact with their own 3D avatars. As orders for virtual bodies continued to roll in, she worked with a team of collaborators, including Robert Nideffer, Nathanial Freitas, Kenneth Fields, and Jason Schleifer, to realize this vision, which would become Bodies© INCorporated.
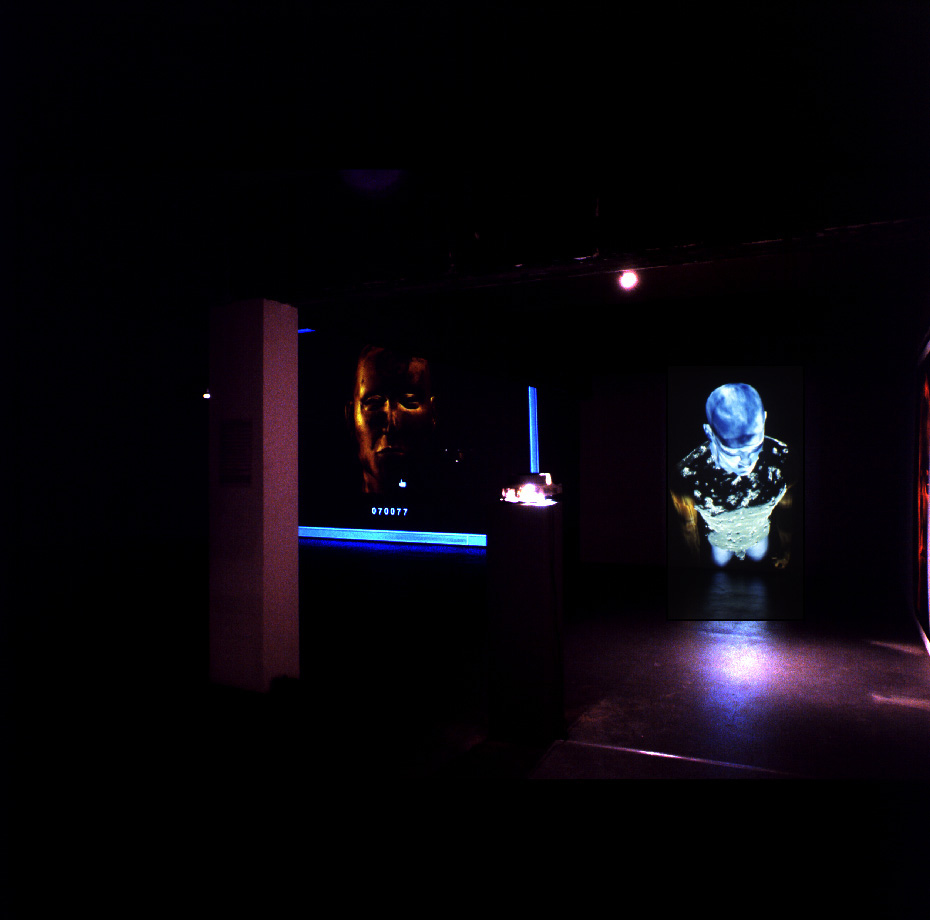 Installation view of Bodies© INCorporated at the San Francisco Art Institute, 1996.
Installation view of Bodies© INCorporated at the San Francisco Art Institute, 1996.
Bodies© INCorporated included a gallery installation, which featured high-resolution prints of 3D avatars, and a web platform where people could construct their own, selecting from an assortment of body parts and adding textures such as “lava” and “blue plastic” to make hybrid 3D assemblages.
The project was developed at a time when the use of graphical avatars became more common in videogames and chat forums. While the use of such avatars is often championed as an opportunity for redefining identity and social relations, Vesna took a darker view, casting them in her project as commodities circulating in a domain controlled by a fictional corporation.
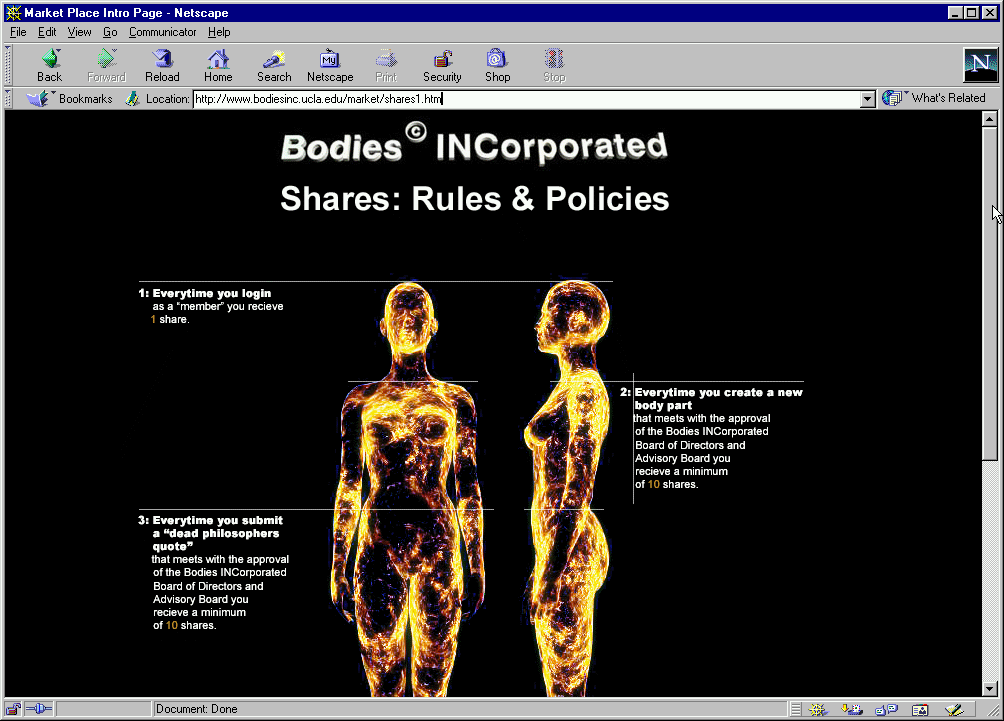
In keeping with this vision, users had to agree to heavy-handed terms and conditions—some of which were borrowed from Disney’s website–before entering the project, essentially giving up all rights to their virtual body.
Vesna sourced body parts from Viewpoint Data Labs, a company that offered CGI bodies for sale to clients such as the Star Trek franchise. The off-the-rack body parts all conformed to prevailing bodily ideals, but they could be assembled in hybridized ways.
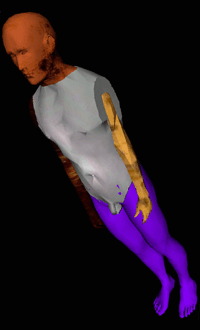 “fritz,” body assembled for presentation of Bodies© INCorporated in Los Angeles.
“fritz,” body assembled for presentation of Bodies© INCorporated in Los Angeles.
The bodies were constructed in VRML, or virtual reality modeling language, which allowed users to interact with 3D graphics in a browser at a very low connection speed. The VRML environments in Bodies INCorporated are all less than 20 kilobytes in size.
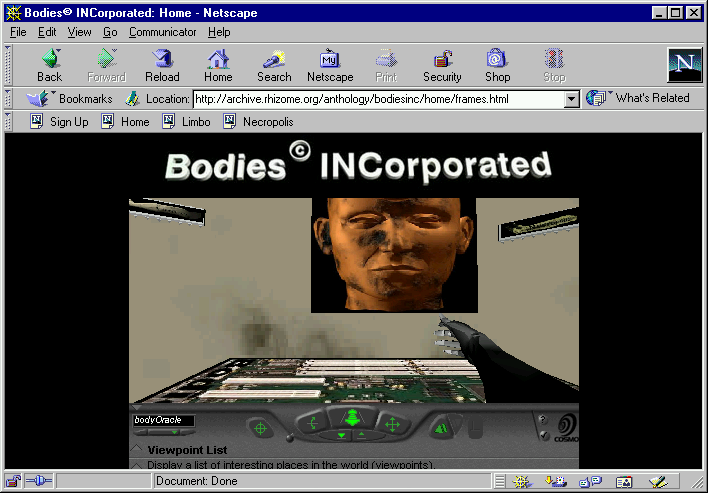
Each body part could be assigned a texture, such as wood, bronze, or glass; these textures placed the bodies outside of traditional racial categories, but each texture also carried with it a set of associations, which often evoked existing archetypes or stereotypes. The chocolate texture, for example, is described as “sweet and moist; the integrative force, interweaving and balancing; marketing element.”
Read 'The Appended Subject: Race and Identity as Digital Assemblage' by Jennifer González (PDF).
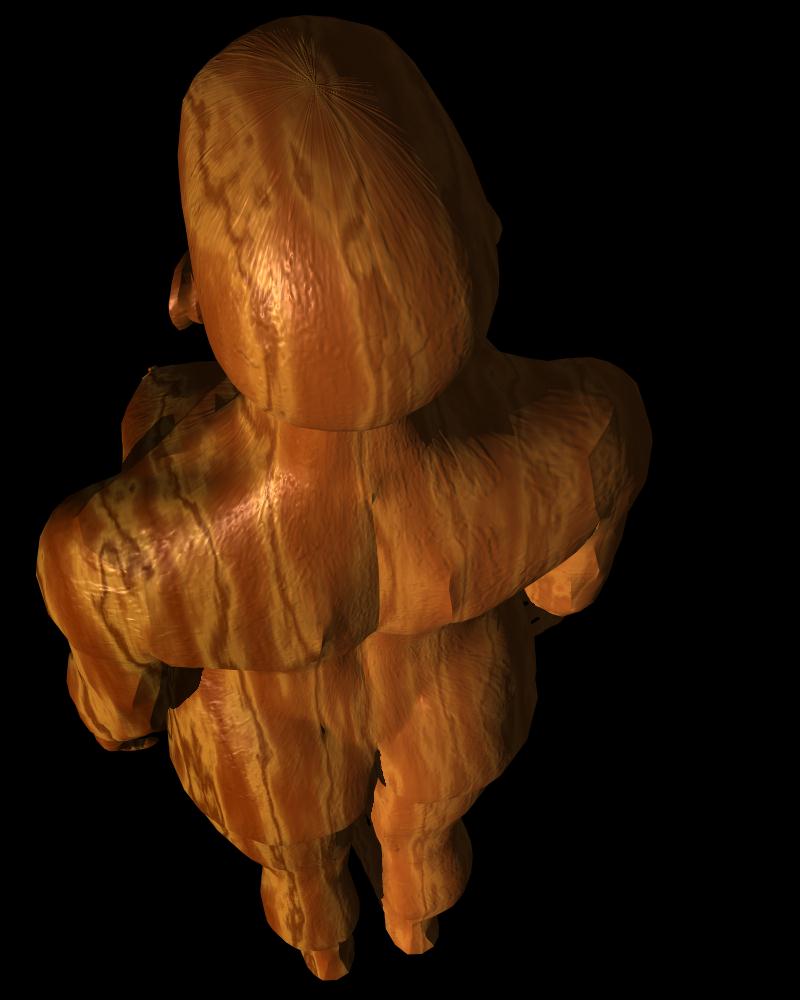 “Wood Woman” from Bodies© INCorporated.
“Wood Woman” from Bodies© INCorporated.
After assembling their body, users could choose to enter virtual environments such as “Home,” which offered navigation to the full site in a 3D environment, “Limbo,” where gyrating cubes of text linked back to completed order forms for virtual bodies, and “Necropolis,” where they could see gravestones designed by users who chose to delete their bodies.
Bodies© INCorporated highlights the way in which the recombinant, hybridized bodies that came to the fore in 1990s culture were still subjected to categorization, stereotyping, and commodification even as they seemed to promise a kind of utopic liberation.
“It remains to be seen whether a ‘recolonization’ of business power is the most effective method for its critique. Bodies© INCorporated succeeds at least in foregrounding relations among bodies, bureaucracy, and power in a culture based on consumption.”
—Jennifer González
Victoria Vesna, Ph.D., is an artist and a professor at the UCLA Department of Design Media Arts. She is Director of the Art|Sci Center at the School of the Arts (North campus) and California NanoSystems Institute (CNSI) (South campus). Trained as a painter (Faculty of Fine arts, University of Belgrade, 1984), she went on to conduct experimental research between and across disciplines. With her installations she investigates how communication technologies affect collective behavior, and how perceptions of identity shift in relation to scientific innovation (Ph.D., CAiiASTAR, University of Wales, 2000). Her work involves long-term collaborations with composers, nano-scientists, neuroscientists, and evolutionary biologists, and she brings this experience to students. She has exhibited, published, and lectured extensively. She is the North American editor of “AI & Society Journal” (Springer Verlag, UK) and in 2007 published an edited volume, “Database Aesthetics: Art in the Age of Information Overflow” (Minnesota Press) and another in 2011, “Context Providers: Conditions of Meaning in Media Art” (co-edited with Christiane Paul and Margot Lovejoy, Intellect Ltd, 2011.)
 A Cyberfeminist Manifesto for the 21st Century
VNS Matrix (Josephine Starrs, Julianne Pierce, Francesca da Rimini, and Virginia Barratt)
1991
A Cyberfeminist Manifesto for the 21st Century
VNS Matrix (Josephine Starrs, Julianne Pierce, Francesca da Rimini, and Virginia Barratt)
1991